
What Are Google Algorithm Updates?
Google Algorithms are a sophisticated system that pulls information from its search index and shows the best results for a right user query. To display relevant web pages on its search engine results pages (SERPs), the search engine employs a variety of ranking variables and algorithms.
Initially, Google made a few modifications to these systems. Now, it is enhanced dozens of times a year in quality improvement for search results. Though many updates are small, major google algorithm updates like Panda (2011), Penguin (2012), Hummingbird (2013), and BERT (2019) revolutionized ranking and display for search results.
In this article, A True Marketers explain the major google algorithm updates, their importance, how to approach them, and more.
Key Takeaways
- Major Google algorithm updates continually change the ranking of websites with an increase in emphasis on content quality, user experience, and authority.
- Understanding what are Google Algorithms are enables businesses to adapt themselves to the update and maintain visibility in search.
- The history of the Google algorithm updates clearly indicates a move from keyword-based to intent and relevance-based systems.
- Today, you must stay away from manipulative SEO practices because recent Google algorithm updates penalize unnatural backlink schemes, keyword stuffing, and thin content.
- Stay abreast of the most recent Google algorithm updates if you wish to maintain your website’s visibility in accordance with the ever-evolving ranking factors considered under the major updates such as Helpful Content and Core Web Vitals.
History Of Google Algorithm Updates
Google has a lengthy history of popular algorithm tweaks, search index revisions, and refreshes. Below is a timeline of key history of Google algorithm updates.
1. Early Years (1998 – 2009) – The Birth of Smarter Search
- Back in 1998, Google started changing the game by ranking pages not just by keywords, but by how many other sites link to those pages.
- Simple logic – If many trusted sites link to a page, it should probably rank higher.
2. 2010 – 2012: Cleaning Up the Internet
- Content was multiplying tremendously, so Google stepped in to clean up the mess.
- Freshened-up and faster search results (Caffeine, 2010); fight against poor content quality (Panda, 2011); and give more local results (Venice, 2012).
- 2012 was apparently the year it finally made serious attempts to attack ‘black hat’ link-building methods.
Important Definition: What is black hat? – Black Hat SEO is an unauthorized practice that helps to manipulate the search engines to rank a particular website or web page.
3. 2013 – 2015: Getting Smarter with AI
- Google would start to somehow understand the meanings behind your searches, not just the words.
- Meaning – even when users are unable to perfectly phrase their queries, it gives better answers.
4. 2016 – 2019: Learning from You
- By applying machine learning, Google gradually analyzed behavior from users to improve response.
- It offered personalized search based on location, device, and habits.
5. 2020 – Present: Putting People First
- Nowadays, it is all about helpfulness, and trustworthy content.
- Pages that are useful, user-friendly, and apparently made with real intent get rewarded by Google.
Have Google Algorithms Actually Undergone Changes?
- From time immemorial, Google algorithms changes which had been relatively simplistically based on mere keyword matching evolved into deeper content quality and intent evaluation.
- Google Algorithms like Panda and Penguin, cleaned up the web from spams and very thin content, while later Hummingbird looked for smart and intuitive search results.
- Of late, the user experience really became the center of attention. The Helpful Content Update (2022) set new standards for rewarding genuinely helpful content while punishing clickbait and AI-stuffed articles.
- The September 2023 update emphasized originality. The March 2024 update focused on helpfulness and quality, stating AI-generated content could rank if it meets high standards for users, not specifically “coming into its own.
Today, the message is very clear: Whether a piece of content is created by humans or AI, it has to be useful, reliable, and meaningful to the users. It does not mean you can rely completely on AI content, it depends on your aim and purpose. Google’s evolution is perhaps a testament to the bigger shift that went from gaming-the-system to genuinely helping people.
Major Google Algorithms And Their Updates
If you have ever wondered why some sites rank better on Google than others, you have to remember that the algorithm is in a constant state of change and update. Consider these updates as some behind-the-scenes improvements that Google performs to provide better and more relevant results for users. Some of those updates come as minor tweaks, but quite a few have taken the SEO world by storm.
Let us go ahead and dissect some of the biggest ones:
1. Panda (Launched: February 2011)
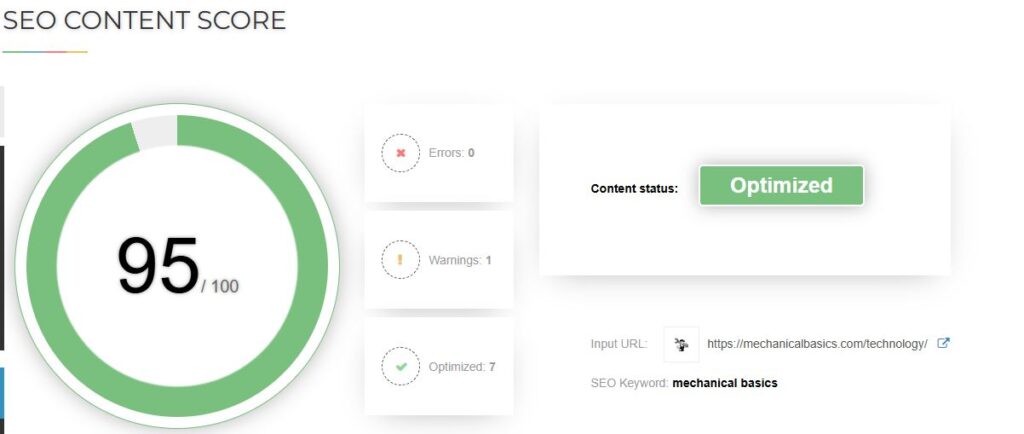
Panda is one of the key google algorithms that is all about content quality.
Before Panda, a majority of websites ranked well just by keyword stuffing or copying content. Panda went into action like a watchdog and penalized thin content sites, copycat sites, or content farms.
It rewarded sites with original, useful, and well-written content. Affected sites saw their rankings drop from super-high to super-low, and sites with high-quality content started reaching the top.
How it works: Panda gives each page a content-quality score and sends this score to the ranking algorithm.
2. Penguin (Launched: April 2012)
If Panda defined content, Penguin, another key Google Algorithm that is introduced to work on finding the spammy links and punishing sites.
Some sites used dirty tactics like buying backlinks or joining link schemes to improve rankings. Penguin is created to punish these manipulative ways. If your site is involved in unnatural or spammy links, it most likely suffers a penalty.
How it works: Penguin analyzes the quality of the backlinks pointing towards a particular site/blog. If there are bad links, the Penguin algorithm will devalue the site.
3. Hummingbird (Launched: August 2013)
Hummingbird, another key google algorithm which changed the entire game.
Instead of matching exact keywords, it tried to understand the intention of the searcher. If someone were to search for the phrase “best way to fix a leaking tap,” Google would now understand the meaning behind the query, not just match the words.
How it works: Hummingbird performs semantic search and natural language processing to give results that are more user intent relevant.
4. Pigeon (Launch Date: July 2014)
Pigeon is the google update, in a quiet manner, truly transformed good local business rankings on Google. It acted as a refinement filter for Google when granting more wholesome location-based search results.
For instance, when someone typed “pizza near me,” instead of meaningless or abstract results, Google started giving truly local options for pizza. It assisted local listing visibility in both Google Search and Maps.
How it works: Pigeon enhanced the connection between Google’s local and core search algorithm to intelligently use location and distance in ranking local results.
5. Mobilegeddon (Launched April , 2015)
Mobilegeddon, the Google Update that sought to enhance search rankings of mobile-friendly sites. Sites that weren’t mobile optimized suffered considerable drops in mobile search results, while responsive pages flourished in gain of visibility.
How it works: In determining rankings for mobile users, mobile responsiveness, load speed, and usability are assessed.
6. RankBrain (Launched: October 2015)
RankBrain – the Google Algorithm which integrated artificial intelligence in its functioning, RankBrain helps Google interpret unfamiliar search queries by understanding the context in which a query is made and with the behavior of the user.
If someone typed something vague or new, then RankBrain could still provide useful results based on patterns it had learned.
How it works: It uses machine learning on search results, particularly when it deals with ambiguous or long-tail queries.
7. Possum ( Launched September, 2016)
The Possum, the Google Update which changed the way local search results entered, particularly in Google Maps and the Local Pack.
How it works: It filters out duplicate business listings and uses the searcher’s location more and more to diversify the results.
8. Fred ( Launched March 2017)
Fred, another key Google Update that punished sites with low value, marked by tons of ads, and filled with affiliate-heavy content.
How it works: It identifies sites where monetization is put ahead of the user experience, specifically sites characterized by thin, repetitive content.
9. Core Update (Launched: March 2018)
In Core Update, the focus is on improving the quality of search results by promoting content that is helpful, accurate, and relevant. In 2025, it further gives less concern toward origin, whether human or AI-generated, and values more on content.
How it works: This update has worked on its underlying systems to create an evaluation of helpfulness and quality for both human- and AI-generated content, thus putting the usefulness on top in the hierarchy.
10. Medic (Launched on August, 2018)
Medic, a much larger Google Update that heavily targeted health, finance, and other “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) sites.
How it works: It gave great emphasis to E-E-A-T—where the main emphasis was on experienced, trustable, and authoritative content.
11. BERT (Launched: October 2019)
BERT is the Google Algorithm that made great strides in language comprehension.
It enables Google to comprehend the full context of a word in a sentence, particularly in complicated or conversational searches. Hence, for the query “Can you get medicine for someone at the pharmacy?” would return better results.
How it works: BERT applies deep learning to natural language in a way that resembles human understanding.
12. Core Web Vitals (Launched: June 2021)
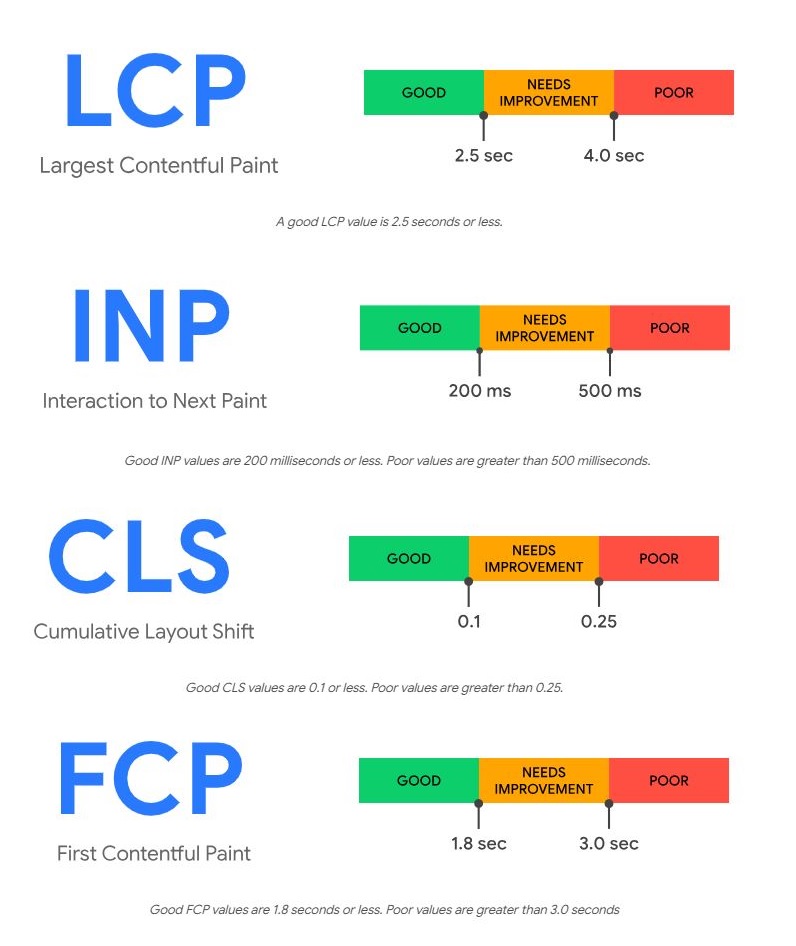
Core Web Vitals is a part of Google’s Ranking Algorithm.
This update kicked off orienting SEO towards user experience.
Google began ranking sites not just for what they say-but how well they perform.
A trio of critical factors were introduced in this update:
- loading speed
- interactivity (how responsive a site feels), and
- visual stability (how smooth things appear while scrolling).
Before this update, having great content was the only thing needed; being fast and free of any frustrations was less important.
How it works: Google uses Core Web Vitals as measurable metrics to assess user experience, and those signals are now partially used to rank.
13. Helpful Content Update (Launched: August 2022)
With this Google update, content creators were instructed to write for people and not for Google alone.
Such sites full of SEO tricks but providing little to no value started losing ranks. Now, Google looks for content that is truly helpful, original, and written by someone with hands-on experience or expertise.
How it works: It acts through a site-wide signal identifying content created not to help users but to achieve ranking.
14. SpamBrainc (Ongoing- Launched in 2018)
SpamBrain is an ongoing effort to counter web spam and low-quality content in search results.
How it works: it employs machine learning to try, detect and filter manipulative practices such as link spam and cloaking so that only relevant and trustworthy content would get ranked.
15. Core Updates: (2017–present)
How it works: As early as 2017, Google began referring to larger updates as Google core updates. Since then, there has been even less transparency about what those upgrades are and which aspects of search they are designed to enhance.
SEOs frequently track post-update ranking movements to determine what exactly has changed, but there is rarely a definite observation.
Google core updates are most likely just improvements to earlier Google updates, although they could be bundles of smaller updates coupled together.
Recent Google Core Updates
- Core Update March 2025 – The goal of this common core upgrade was to make search results more relevant and helpful.
- Core update March 2024 – Being aimed at assessing genuine helpful content while negating all forms of low-quality, AI generated, or unoriginal material.
- Core update November 2023 – Enhanced the Helpful Content System to foreground people-first, and original content.
- Core update October 2023 – Targeted manipulative SEO tactics and debuted alongside a spam update meant to demote unhelpful content.
- Core update August 2023 – Fine-tuned E-E-A-T signals; sites having outdated or low-expertise content encountered losses.
- Core Update March 2023 – Rewarded the creation of high-quality, relevant content; sites having thin or overly optimized pages were hit hard.
Why Is It Important To Stay Updated With Recent Google Algorithm Updates?
- Protect your ranks: According to what Google is changing, you get ample time to work on it so as to not undergo a sudden rank drop.
- Maintain your traffic flow: Updates alter visibility, and so doing, staying aware helps stability in guiding people to your sites.
- Avoid penalties: Rules know-how will definitely get you into trouble.
- Fine-tune your SEO: Optimization-enhanced content is going to be well perceived by Google.
- Stay ahead of others: While the market scrambles for post-updates, you would have had a head start.
Conclusion
Google algorithm updates are very important in allowing sites to be seen and stay trending in SEO. Upon understanding the changes and making content and SEO changes accordingly, it could help a site stay high on search rankings. By keeping oneself updated on the algorithm changes and working through them, you can sidestep penalties, remain highly competitive, and offer stellar content that benefits the user with a willingness to be perceived by Google’s evolving priority.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How frequently is Google’s search algorithm updated?
According to Google, its search algorithm is updated thousands of times a year. Most of the time, Google algorithm changes are too subtle to be seen. However, Google occasionally makes a fundamental update that permanently alters how we do SEO.
2. When did Google reveal a change to its core algorithm?
Updates to Google’s core algorithm were revealed on September 12, 2022 and finished on September 26, 2022. The Helpful Content Update was announced by Google and went live on August 25, 2022.
3. Can you explain what Google algorithms are?
Google’s algorithms are a sophisticated system that pulls information from its search index and provides the best results for a query right away. To display relevant web pages on its search engine results pages (SERPs), the search engine employs a variety of ranking variables and algorithms.
4. What is the most recent 2025 core update update?
It began on March 13, 2025, and was finished on March 27, 2025, around 14 days later. In order to improve the relevance and usefulness of search results, Google regularly improves its basic ranking mechanism. This update was no exception.
5. Which three ranking elements are most important to Google’s algorithm?
Google’s ranking system takes into account a number of variables, but three in particular—content quality, backlinks, and user experience—stand out. These elements assist Google in identifying the websites that are most useful and pertinent to users looking for particular information.
