
Want to increase your site’s visibility on Google?
This Google Search Console guide is here to help. If you are a novice or want a quick refresher, understanding what is Google Search Console, how to add property in Google Search Console, and how to use Search Console effectively, etc. can help immensely.
Google Search Console is a free tool from Google to track organic performance, fix indexing issues, optimize content, and more.
A True Marketer’s Google Search Console guide will lead you through the setup, features, and tips for every level with concrete steps and Google Search Console help.
Key Takeaways
- This Google Search Console guide provides a step-by-step overview of setup, features, and optimization tips designed to enhance any site’s search performance.
- To get started, learn how to add property in Google Search Console by domain or URL prefix and verify it by an HTML tag, file upload, or DNS.
- Google Search Console features Performance, Indexing, Mobile Usability, Core Web Vitals, and Backlinks to enhance ranking and fix issues.
- Discover how to use Search Console to find low-CTR keywords, refresh low-performing pages, and improve mobile experiences.
- Unlike paid tools such as Ahrefs and Semrush, GSC relies on trusted first-party data complemented with built-in Google Search Console help.
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (simply GSC) is a free organic tool that assists you in tracking the technical SEO health and search engine optimization performance of your website. Apart from monitoring technical SEO health, GSC gives information about the indexing and ranking of your site, helps to diagnose issues affecting visibility, and offers tools to further optimize content and site structure for better ranking potential.
Simply, Google Search Console acts as a bridge, interpreting how search engine users interact with your website and mediating the insights Google provides to optimize your presence.
It can enhance your website and increase Google traffic.
Some of the things you can accomplish with GSC are as follows:
- Examine and show up your website’s organic performance in search results.
- View the pages on your website that Google can locate and index.
- URL inspection and submission for faster indexing, along with submitting XML sitemaps.
- Find technical SEO mistakes.
- Understand how Googlebot views your pages, and spot rendering issues.
- Backlink profiles and internal linking structure analysis.
- Use of rich results and schema markup insights to improve the site appearance.
Here’s your Google Search Console guide to boost your SEO in this article.
How to Set Up Google Search Console?
Setting up GSC cannot be any more straightforward. Just follow this step‑by‑step Google Search Console guide:
Step 1: Sign into GSC
Head over to Google Search Console and log in through your Google account.
Step 2: Add Your Property
You can select your property either as a Domain Property or URL prefix
- In Google Search Console, a Domain Property covers all protocols (http/https), subdomains, and paths beneath a domain such as example.com or m.example.com. So it gives you an overall picture of the domain itself.
- On the other hand, a URL-prefix Property specifies a protocol and can include a subfolder, like https://example.com/blog/. It provides data strictly for that particular URL structure (either https or http, whichever you ask/submitted for). You can choose if you want full coverage of the domain or just one section tracked.
Put in your Domain or URL prefix and click Continue.
Step 3: Verify Site Ownership
Google Search Console has various verification methods. The table below should aid you in picking what fits your situation.
| Ways To Verification | Suitable For | Explanation |
| HTML file upload | URL Prefix Property | Relatively straightforward but needs a file upload ability to publish on your site at the specific URL. Might not be available on specific site hosting platforms. |
| HTML tag | URL Prefix Property | Relatively easy, but the ability to edit the HTML source code of your site’s homepage. Might not be available on certain site hosting platforms. |
| Google Analytics tracking code | URL Prefix Property | Fairly straightforward if the page already has a Google Analytics tracking code for a Google Analytics account you can access. In cases where it does not have a tracking code, then you add one (might involve creating a Google Analytics account if you don’t already have one). |
| Google Tag Manager |
URL Prefix Property | The process is simple if the website already contains a Google Tag Manager snippet for an accessible Google Tag Manager account. You will need to add a snippet if the page doesn’t have one, which can mean making a Tag Manager account if you don’t already have one. |
| Google Sites or Blogger Account | URL Prefix Property | In case you have made your site through Google Sites or Blogger and, meanwhile, are logged in with the same Google account, Google ordinarily takes care of verification for you. No further action is necessary. |
| Domain Name Provider | Domain Property Verification | Domain property verification is done via DNS. If your domain provider is available in the verification wizard, the procedure becomes easier. Simply copy the TXT record in the GSC and add this via the Domain name provider’s dashboard to the DNS settings. Allow time for the DNS to propagate (max 48 hours), then click ‘Verify’. This verification method works for all protocol (http/https) and subdomain variations of your property. |
Step 4: Wait For Verification
- Domain Name Provider: DNS changes may take up to 48 hours, so if it does not pass the first time, come back later and hit Verify again.
- HTML File Upload (URL prefix): Usually an instant verification, but it could take a couple of minutes.
- HTML Tag: Verifies within minutes once the tag is correctly added to the homepage.
- Google Analytics: Instantly verifies if the tracking code is active and accessible.
- Google Tag Manager: Instant verification if the container snippet is correctly added.
- Google Sites or Blogger: Often automatically verifies when you’re logged in.
Step 5: Access Your Dashboard
Once verified, the Search Console help kicks in. Access the important reports like Performance, Coverage, and Sitemaps to start tracking and optimizing your site.
Key Features & Reports in Google Search Console
Understanding the core tools within GSC is probably the utmost important when it comes to utilizing it. The features and reports in Google Search Console are:
1. URL Inspection Tool
Check the index status of any given page instantly. It is used in seeing how Google crawls and renders your content and fixes issues fast.
2. Performance Report
View data on total clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position. It learns how to use Search Console to improve SEO by looking into top queries, top pages, countries, and devices.
- Search Results
Show your site’s performance in Google Search, including learned clicks, impressions, CTR, and position of keywords. Helps evaluate SEO impact.
- Discover
Shows the performance of your content in Google Discover, including impressions and clicks coming from mobile feed-based traffic.
- Google News
Keeps track of the news content appearing in Google News along with the user engagement, impressions, and clicks.
3. Indexing
- Pages
Lists all indexed, excluded, or error pages with reasons such as 404, redirects, or crawling issues. Known as the Coverage Report.
- Videos
Reports issues related to video indexing, like missing structured data or non-detectable videos by Google.
- Sitemaps
Submit XML sitemaps to enable Google to find and crawl your content better. A must-do step after adding a property in the Google Search Console.
- Removals
Temporarily blocks a URL from Google Search, useful when an outdated or sensitive content needs to be taken down quickly.
4. Experience
- Core Web Vitals
Measures real-user performance metrics for Core Web Vitals like LCP, INP, and CLS affecting page speed, stability, and user experience.
- HTTPS
Displays whether your website is served securely using HTTPS. Flags issues such as mixed content or invalid SSL certificates.
5. Enhancements
- FAQ
Checks structured data for FAQ pages to qualify for rich results in Google Search. Reports errors or validation issues.
6. Manual Action Report & Security Issues
- Manual Actions
Lists Google penalties applied for violating search guidelines, which might include spam, cloaking, or unnatural backlinks.
- Security Issues
Flags serious threats such as hacked content, malware, or phishing present in your website, which affect visibility and trust.
7. Links
Who links to your site (backlinks); your most linked pages; anchor text; SEO internal linking analysis.
8. Mobile Usability
Detects problems that compromise the mobile browsing experience of the site. Since mobile-friendliness is a ranking factor, this helps in optimizing the site accordingly.
Note:
There are few other features in Google Search Console that could appear beyond the ones listed above. They are revealed based on the type of your website and the kind of traffic it receives, thereby giving site-specific insights and tools as needed.
How to Use Google Search Console to Improve SEO?
After setting up your website in Google Search Console (per the installation guide), you are now ready to use Search Console and get your SEO fixed. The steps are
1. Discover High-Traffic Keywords
Use the Performance Report and filter the keywords preventing traffic. Analyze the metrics that include impressions and CTR. If a keyword gets a large number of impressions but a low CTR, then it’s time to change its page title or meta description to improve clicks. This is probably the very instance when you want to put your knowledge of using Search Console to good use.
2. Fix Under-Performing Pages
Pages with low average positions and high bounce rates can be fixed by updating their content, adding internal links, or changing the keywords they are optimized for. This is well-identified under the “Pages” tab of the performance section.
3. Submit Updated URLs
After updating a page, use the URL Inspection tool to submit the page for re-indexing. This helps expedite indexing and ensures that Google picks up your changes quickly– one of the great Google Search Console help
4. Optimize for Mobile
Review the Mobile Usability Report and resolve issues such as clickable elements being placed too close to each other, and texts being too small. Mobile-friendliness is essential in rankings and in providing a quality user experience.
5. Enhance Page Experience
The Core Web Vitals display metrics such as page speed and visual stability. Fix poor scores by applying technical SEO fixes: image compression or limiting third-party scripts.
6. Keep an Eye on Backlinks
In the “Links” report, check which domains link to your site, or rather, websites that link to specific pages on your site. For future content strategy, refocus on pages with the highest-quality backlinks.
By applying the above steps, not only you learn what Google Search Console is, but you also actively employ the tool in boosting your visibility. Whether you have just learned how to add property in Google Search Console or are fine-tuning an existing setup, these steps always guarantee positive SEO outcomes.
Common Issues and How to Fix Them
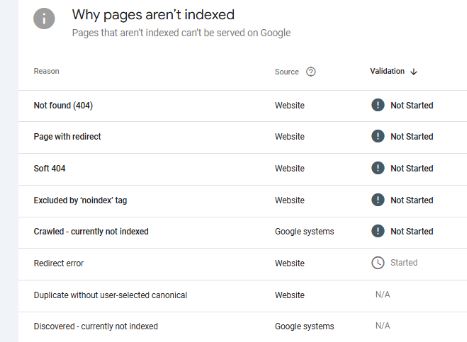
1. Server Errors (5xx)
These indicate internal server-side problems. Visible under the Pages report with reasons like Server Error (5xx).
How To Fix: Check your server logs, rollback any recent changes, make sure your server has enough resources or contact your hosting provider.
2. Not Found (404)
It happens when Googlebot encounters pages giving “Not Found” errors.
How To Fix: Establish 301 redirects, clean up broken or internal links, and update or remove outdated sitemap entries.
3. Unauthorized (401)
Shows up when pages require authentication or block Googlebot access.
How To Fix: Adjust authentication settings, whitelist Googlebot, and ensure no IP or user-agent restrictions.
4. Soft 404
Pages that return a 200 status code but are effectively empty or misleading (e.g., thin content or custom error pages).
How To Fix: Improve content quality, correct any misleading redirects, or ensure error pages return proper status codes.
5. Redirect Errors
Includes issues like chains, loops, or incorrect redirect targets.
How To Fix: Simplify chains, eliminate loops, use suitable status codes (302 vs 301), and update internal links.
6. Blocked by robots.txt
Googlebot is prevented from accessing pages due to disallowed instructions.
How To Fix: Update your robots.txt file to allow crawling of important pages, then request a re-crawl.
7. Core Web Vitals Issues
Performance problems flagged under the Experience report (e.g., LCP, INP, CLS).
How To Fix: Optimize page speed, improve stability, and enhance interactivity following the Core Web Vitals guidelines.
8. HTTPS Errors
Pages served over HTTP instead of HTTPS.
How To Fix: Secure your site with SSL, update links to HTTPS, and resubmit URLs via GSC after changes.
9. Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
The pages have a no-index tag to prevent Google from displaying them in search results.
How To Fix: Remove the no-index tag on all important pages that you want to be indexed.
10. Duplicate without user-selected canonical
Google has found similar pages for which none is specified as a canonical tag.
How To Fix: Provide canonical tags signaling to Google which version of the content to index.
11. Discovered–currently not indexed
Google found the URL but hasn’t crawled or indexed it yet, often due to crawl budget or low priority.
How To Fix: Build authority for your site, link to the page internally, or submit the page via URL Inspection.
12. Manual Actions
Penalties imposed on human reviewers for things like spam, unnatural linking, or cloaking.
How To Fix: Fix your site to be free of violations and then request a review through GSC.
13. Security Issues
Flags on your site say “malware”, “hacked content” and “phishing detected on your site”.
How To Fix: Clean malware, fix security vulnerabilities, and submit a security review in GSC.
How is GSC different From Other Organic Search Performance Tools?
Read on How Google Search Console is different from other tools like Semrush, Ahref, and Moz.
1. First-Party Data vs. Estimates
Unlike Semrush, Ahrefs, and Moz, which depend on third-party crawlers, clickstream, and estimation, GSC gives correct, real-user data straight from Google (clicks, impressions, CTR, position).
2. Diagnostics & Indexing Control
Uniquely provides information on crawl errors, index coverage, Core Web Vitals, manual actions, etc.; not seen in any other platform.
3. Ease and Cost
As a free tool, GSC is fairly easy to set up and free of hassle. Semrush provides thorough competitor analysis, Ahrefs excels at backlink tracking, and Moz provides affordable keyword research—yet all are paid subscription services!
4. Best use cases
The GSC can be used for site-specific diagnostics and precise performance tracking, while Semrush and Ahrefs are used for broader market awareness, keyword search, competitive insight, and backlink research.
Conclusion
Knowing what Google Search Console is, how to add Property in Google Search Console, and how to use Search Console which means you can keep an eye on your site’s health, fix issues, and improve rankings.
While Semrush and Ahrefs can give other views, GSC remains the best source for accurate, first-party information to track and fix organic issues, keep your site healthy and structured. For continual support, use the built-in Google Search Console Help to stay search-engine ready.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Google Analytics set up in SEO?
If you do Google Analytics for SEO, setting relevant Data Streams will form the basis of your efforts and activities. Data Streams are pipelines that dictate how data flows through your GA4 Property.
2. What is GA4?
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the newest web and application analytics platform from Google. It replaces the older version, Universal Analytics (UA),and presents more exhaustive mechanisms to monitor how human actions on websites and apps take place. Being an event-based data model, GA4 is much more flexible and provides deeper insights into user interactions. Among some other notable features, it offers cross-platform tracking, AI-powered insights, and controls privacies.
3. How to Fix Crawl Errors in Google Search Console?
In the updated Google Search Console, to fix crawl errors, go to Indexing → Pages. Find errors like 404s, server errors, or blocked resources. Fix them by repairing the links, changing redirects, or changing servers. Then, once you’ve fixed these, hit Validate Fix to let Google know and prompt them to re-crawl the concerned URLs.
4. Are Google Analytics and Search Console the Same?
Both tools are set up by Google for website analysis for free, yet they are focused on different aspects. These two tools are complementary: while Google Analytics will give the website owner useful information about user behavior on his or her site, Search Console details how well the website performs in Google’s search results.
5. What other name does Google Search Console go by?
Google Search Console (renamed in May 2015), formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools, is an online tool that lets webmasters check search queries, indexing status, crawling issues, and how visible their websites are.
