
For SEO, digital marketing, and content creation, an understanding of how search engines work is therefore extremely important so that beyond being able to bring companies up for search, they may in turn present those results to the actual targeted audience.
General Stages of Information Search Process (ISP):
- Task Initiation – The user realizes a need for information.
- Topic Selection – A general subject is chosen for exploration.
- Exploration – Broad searches begin; confusion is common.
- Focus Formulation – The user refines the topic for clarity.
- Information Collection – Collecting all relevant and detailed information.
- Presentation – The final results are logically arranged and will be shared or used.
This article from digital marketing experts will provide information on How do search engine works, stages of search engines, search engine layout, and more.
Key Takeaways:
- Search engines undergo these operational search stages: crawling (discovery of content), indexing (organizing it), and ranking (giving preference to results).
- Content has to be crawled and indexed to get visibility in the search engine index.
- Ranking of pages is carried out by search engine algorithms with factors like keywords, quality of content, and user experience.
- Thus, it is crucial to know How Google Search engine works to enable content optimization for wider reach and traffic.
- Visibility and user-interface interaction are affected by the actual search engine layout including ads, snippets, and organic search results.
What Are Different Search Engines?
There are Abundant Search Engines and each with their own Search algorithm, layout, and user experience. Some major search engines are:
- Google (Launched in 1998):

Currently tops the list as the most used search engine, it is known for its clean layout and powerful algorithms that give the results with an AI overview
- YouTube (Launched in 2005):

While primarily used for video purposes, it runs second to being the largest search engine in the world, guiding users discover their through keyword searches and intelligent recommendations.
- Bing By Microsoft (Launched in 2009):
The search engine owned by Microsoft . It has a more visually appealing layout with heavy integration into Windows and Microsoft services.
- Yahoo (Launched in 1995):
One of the earliest internet pioneers is now using Bing’s algorithm while still keeping its own layout and content ecosystem.
- DuckDuckGo(Launched in 2008):
It is all about privacy, clean layout ad-light, and no tracking of users.
- Baidu(Launched in 2000):
Being the most prominent search engine in China, it caters to the needs of Mandarin speakers and prioritizes locally hosted, culturally relevant content in its search engine index.
- Yandex (Launched in 1997):

Popular among Russians, known for processing the local language and being culturally relevant.
- Ecosia (Launched in 2009):
An eco-conscious company that uses Bing’s algorithm and plants trees with its ad revenues.
- Brave Search (Launched in 2021):

Has ad-free options and puts a strong emphasis on the privacy of its users, with a straightforward design principle.
The layout may change depending on a platform; however, most of these emphasize simplicity in design, the feeling of completeness in speed and need, and have that user-friendly approach.
Specific Other Search Engines:
- Startpage: Search results powered by Google with enhanced privacy; no IP logging or search tracking.
- Qwant: One of France’s search engines promoting user privacy and does not track queries.
- Swisscows: An engine that respects family-friendly and privacy needs and filters violent or explicit content.
- Mojeek: Rare independent search engines that avoid taking services of Google or Bing; indexes its own web independently.
- Wolfram Alpha: The computation search engine which gives factual answers and data analysis instead of giving links to websites.
Different Search Engines Usage Statistics and Leaderboard
- Nearly 92% of the worldwide market is generally held by Google, given its exceptional algorithms, speedy response time, and high reliability on the layout of its search engine.
- Bing is at number two with approximately 3% of the market share and most often favored by Windows users.
- Yahoo and DuckDuckGo capture about 1%; Yahoo has its legacy audience while DuckDuckGo has privacy-seeking users.
- In China, Baidu has about 70% of the Chinese market, being the top search engine.
- Yandex is the dominant search engine in Russia, with over 60% of the local website traffic share. Highly competent in Russian language processing and understanding local taste, it thus remains the first choice of users in Russia and adjacent regions.
Why Google Holds the Lead?
- Maintains clean layout of the search engine, be it desktop or mobile.
- The indexing system uses advanced algorithms to crawl and index billions of web pages within a very short time.
- Google continuously improves through AI and ML keeping the search engine for better personalization.
- Understanding how Google Search works, highlights its unrivaled speed and relevance.
- Giving out wide-ranging options of Google products from Chrome, Maps, Ads, YouTube, and Gmail.
- Being served together with other tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and learning platforms such as Google for Education and Google Scholar.
Google is the most advanced indexing system, has the best UI, has the fastest response time, and is forever evolving via AI, which has made it the world’s default search engine.
The 3 Core Stages of a Search Engine
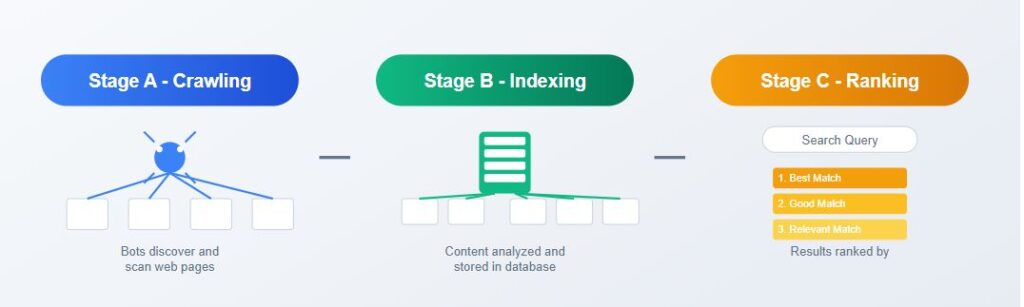
Search engines work through three core stages:
Stage A – Crawling
Stage B – Indexing, and
Stage C – Ranking.
These stages exist to ensure an accurate presentation of relevant information to the user for their queries.
Stage A : Crawling
The first step from the search stages is crawling:
Search Engines discover new or recently updated content on the web. They use automated programs called bots, or spiders -for instance, Google Bots scan the websites and follow links from one page to another.
These bots move across billions of pages to locate valuable content.
How Google Search works begins with crawling because this stage is where Google’s data collection occurs, which is later stored during indexing.
A website that is well structured is easier to crawl, making Google’s job easier.
Search Engines assign crawl budgets-limitations on the number of pages to be crawled on a site-based on how efficiently resources (i.e., the search crawler itself) are being used. Crawl budgets are wasted on bad site structures or broken links, which get you less visibility.
Having a great technical foundation ensures all your valuable content is found during this initial search engine step.
Stage B: Indexing
Indexing is the procedure wherein the crawled data is analyzed, classified, and placed into the search engine index-an enormous digital library of online content.
“To understand what indexing is – imagine that a book is being filed within a library so it may be retrieved when needed. The search engine takes into account several items, such as the page’s content, titles, images, and meta tags, to determine the relevance of a query in terms of the user.”
Factors affecting indexing may include:
- The duplicate content may be ignored or de-ranked by the search engine.
- Site speed and mobile-friendliness increase crawl rates and aid successful indexing.
- Clean and valid HTML helps bots extract content correctly.
- Internal linking helps in the discoverability of its deeper pages.
- Sitemaps and robots.txt instruct the bots on what to index or disallow.
- Thin or low-quality content might be one excluded from a search engine index.
An indexed page is more likely to appear in search results, and thus, the process of indexing is the very backbone of digital information storage and retrieval.
Stage C: Ranking
Once indexed, search engine algorithms determine the ranking of content for relevant queries. They are complex formulas that weigh hundreds of factors to determine the most useful and relevant results for a user query.
Some of the signals considered are
- keyword relevance
- backlinks
- content quality, and
- user engagement.
- user experience
How Google Search works right now is by using AI-based search systems such as BERT (for understanding natural language) and RankBrain (to interpret user intent).
Understanding how Google does it gives businesses an edge in optimizing content to match behavior in searching. Ranking is mainly where all earlier steps, such as crawling and indexing, come to the foreground to provide the best content to the user.
What Is Search Engine Layout: What You See vs. What Happens Behind the Scenes
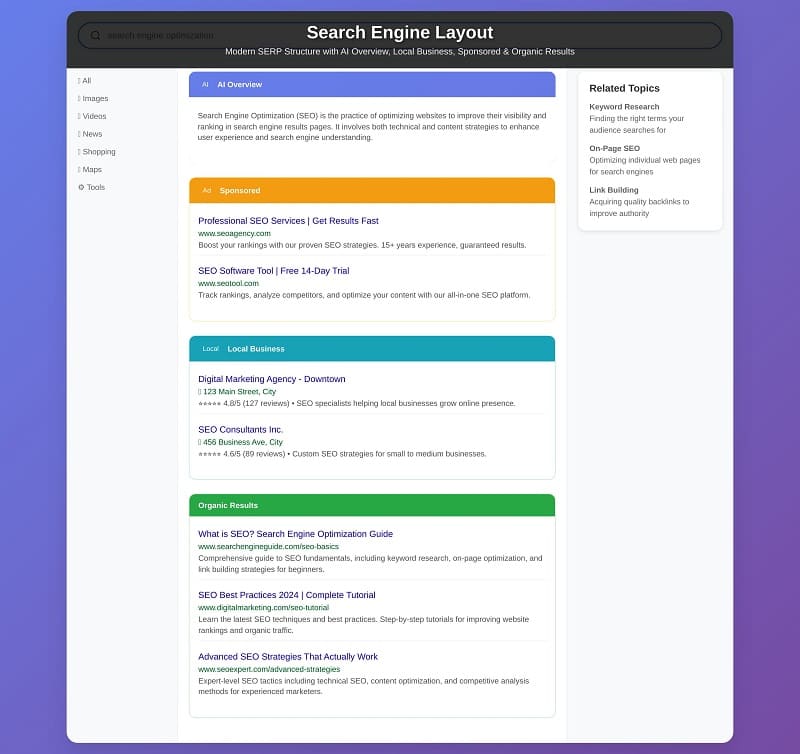
The layout you see when you type a search engine query is made up of multiple visual components including:
- Paid ads (typically positioned atop and below)
- Organic results ranked in terms of relevance, the so-called featured snippets, People Also Asked sections, and knowledge panels.
- AI Overviews
- Sponsored Ads
On the back of such a user-friendly page layout is a series of complicated processes that occur.
As soon as the query is typed into the search box, the search engine swiftly fetches most relevant results from its search engine index, ranks them according to the search engine algorithm, and displays these for your reading pleasure in real time. This involves making sense of user intent, putting hundreds of ranking factors into value judgments that concern usefulness and relevance, and showing the best results within milliseconds.
Knowing the Search Engine layout helps
- Users identify which ones are ads and which are genuine content.
- It helps SEO professionals optimize their pages for various visibility points such as snippets or panels.
- Mobile vs. Desktop Strategy Maximization: Layout and arrangement are different in different devices. Knowing this difference would, therefore, allow web designers and marketers to tweak this for their mobile-first experience and ensure it is visible at the top.
- User Experience With Better CTR: With clear knowledge about layout positions, brands can emphasize the information-the titles, description, schema markup) strategically—boosting click-through rate (CTR) and reducing bounce rates.
Why Understanding Search Engines and Search Engine Layout Important? (for Users & Digital Marketers)
Understanding how search engines work and how the search engine layout is structured can seriously enhance your content strategy.
It teaches users to search smarter and critically examine sources.
Why It Matters:
- Smarter Search Behavior: Users become more efficient and critical in evaluating search results when they know about search stages and layout structures—for example, when differentiating ads from organic results and snippets or panels.
- Better Content Strategy: Digital marketers and SEO experts use the knowledge with regard to crawling, indexing, and ranking to position content well on the Internet-the-more visibility it gets, the more impressions and engagements it gets.
- Technical SEO & Optimization: The more that you know about the role structured data, mobile-friendliness, and page speed play in your visibility, the more you are able to boost your chances of achieving that first rank.
- Increased ROI: If they want to increase the click-through rates and the performance of their campaigns, marketers might want to make use of the knowledge about search engine layout and align their content to how platforms display results.
- Search Intent Mapping: Professionals can optimize marketing by more accurately mapping and predicting how users behave during their information search.
Conclusion
In this way, knowledge of how search engines crawl, index, and rank your content and how those results are displayed via a layered layout will offer a crucial advantage in digital visibility. This power can work for you whether you are literally very knowledgeable or just know how to browse intelligently.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the architecture of a search engine?
A typical search engine architecture includes three components: crawler, indexer, and query processor. The crawler discovers and downloads web pages from the Web; the indexer processes the information and stores the content; and the query processor handles user queries and retrieves relevant search results from the index.
2. Which five steps make up a search strategy?
The following steps comprise the fundamental search strategy:
- Determine the subject of the search.
- Decide on the format for the desired result.
- Describe your search strategy.
- Carry out the search strategy.
- Examine and present the findings.
3. Which two components make up a search engine?
A searchable database of web content is what search engines are. They consist of two components: the algorithm, which is the program used by the search engine to match your query with an index result, and the index, which is a digital repository of data on the web sites.
4. Is YouTube a search Engine?
Yes, YouTube qualifies as a search engine and is frequently ranked as the second-largest search engine, behind Google. Although YouTube is mostly used for uploading videos, its extensive search feature lets users look for certain videos using keywords, just like they would on Google.
5. Which search engine doesn’t have any limitations?
Brave uses their own custom-built index to produce results. No hidden techniques or algorithms, no prejudice or censorship.
6. Which search engine is the most private?
Startpage of the top private search engines. Because of its excellent search results and dedication to customer privacy, Startpage is among the greatest substitutes for Google. Otherside, DuckDuckGo is also a private search engine preferred by users
7. Which browser is the safest?
Brave, Tor, and Firefox are widely regarded as the safest choices because of their robust privacy features and dedication to user security, even if no browser is completely safe. Although Chrome and Edge have robust security protections as well, they might put user convenience and speed ahead of privacy.
8. What is a virtual private network?
A virtual private network, or VPN, functions as a private tunnel for your data by establishing a secure, encrypted connection over the internet. This makes it more difficult to monitor your online behavior because your location is hidden and your online activity is protected from prying eyes like hackers or your internet service provider.
